Retinitis Pigmentosa Retinitis Pigmentosa, also know as RP is a rare eye condition that affects the layer of the eye that is sensitive to light – the Retina. Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP) is a genetic disease that is passed on through generations and the type of vision loss varies. Patients suffering from Retinitis Pigmentosa lose eyesight over time but do not become completely blind. It is a rare disease and usually affects both the eyes simultaneously.
What is Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP)?
The retina is a layer at the back of your eye that converts light into
electrical signals, allowing your brain to see the world around you.
Retinitis
pigmentosa (RP) is the term for a group of inherited eye diseases that
affect
your retina.
Your retina consists of special nerve cells that react to light. These cells
include photoreceptor cells such as rods and cones and retinal pigment
epithelium cells. For proper sight, it’s essential that these cells work
together harmoniously. The genetic mutations that cause RP prevent these
cells
from functioning properly.
Since RP is a group of disorders, the visual changes vary among different
people. Most people with RP have low vision and some people go blind. The
vision
changes usually start in childhood. But, sometimes these changes occur so
slowly
that you don’t realize it’s happening. Some people have faster vision loss.
In
some types of RP, vision loss stops at a certain point.
Retinitis pigmentosa generally affects both eyes.
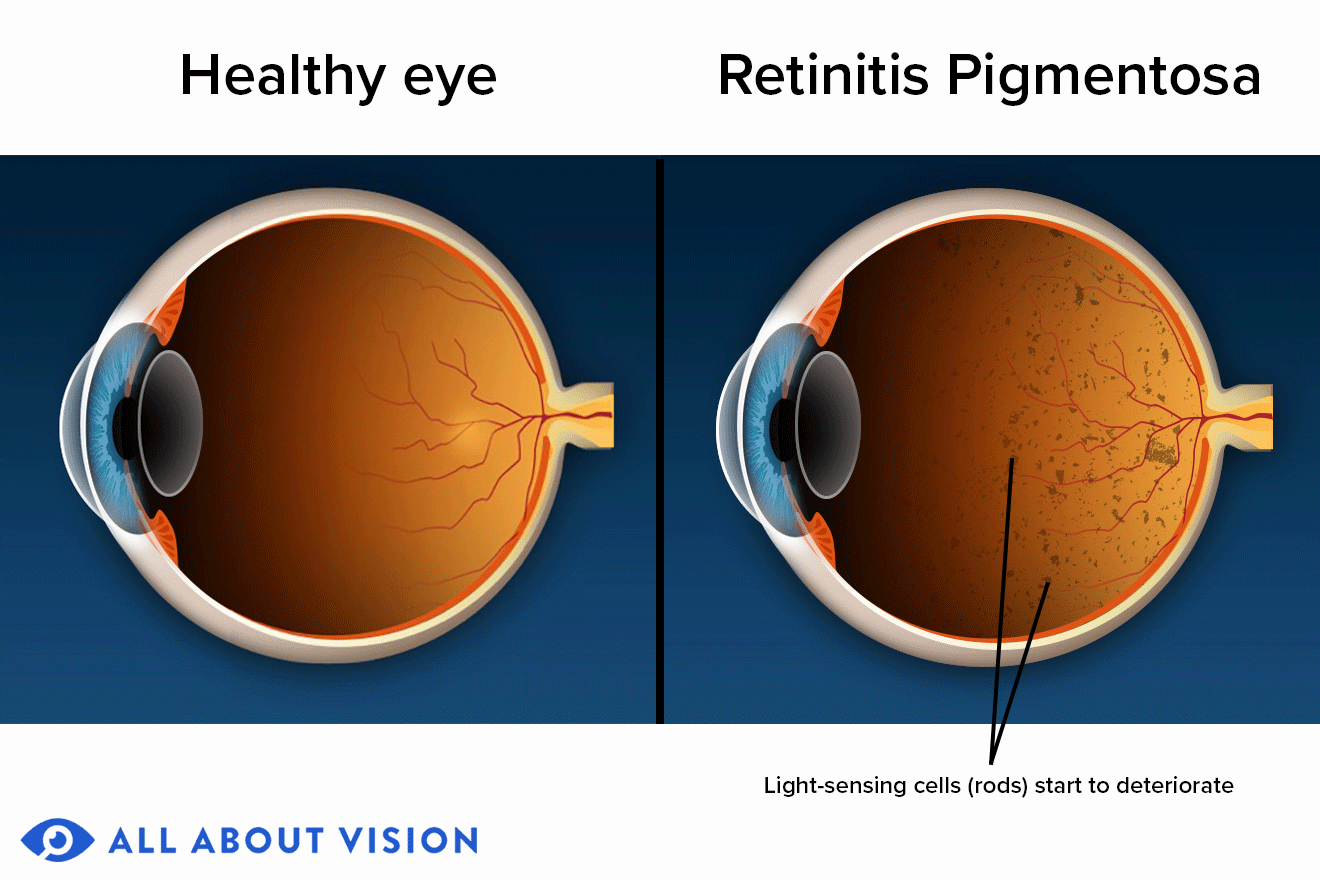
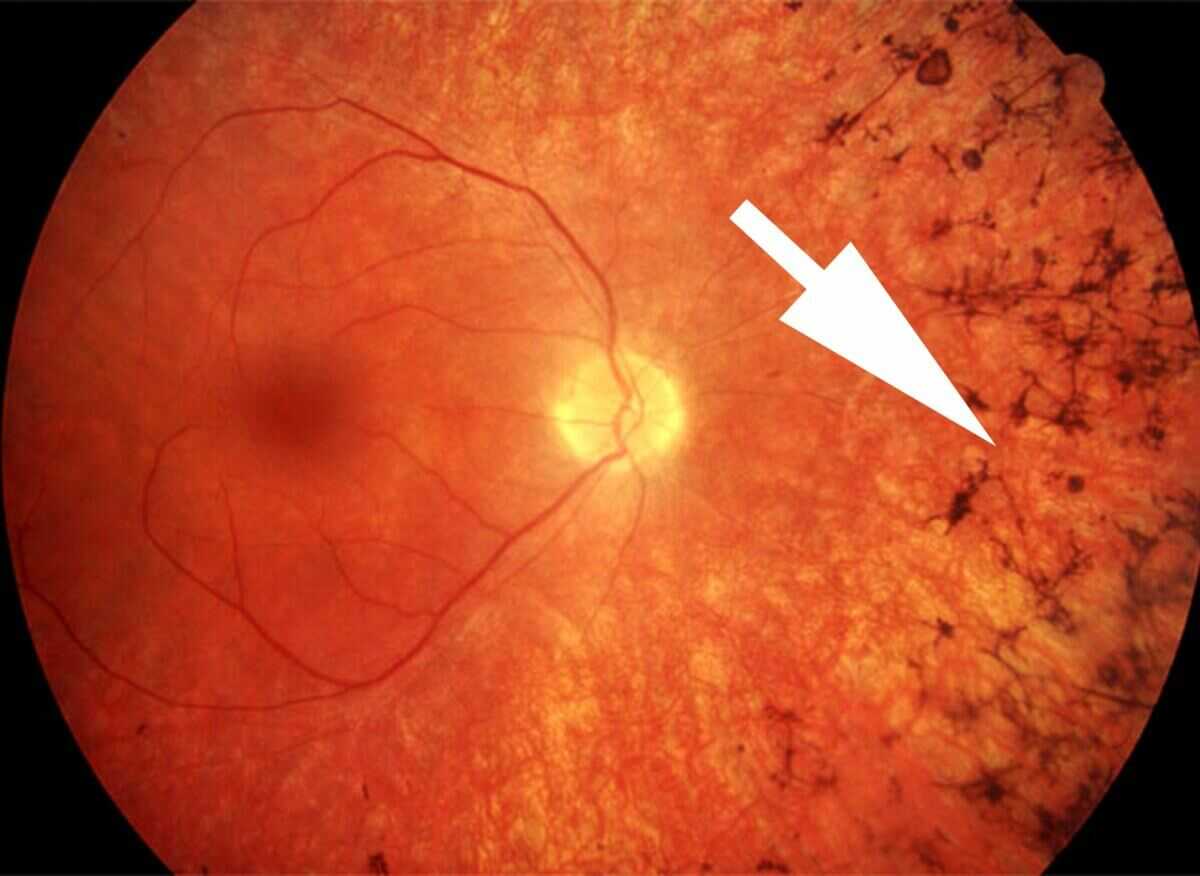
How common is RP? There are an estimated 1 in 3,500 to 1 in 4,000 people in India who have retinitis pigmentosa. Globally, RP affects about 1 in 3,000 to 1 in 4,000 people, or about two million people total.
Signs and symptoms of RP: :
Retinitis Pigmentosa
Early Signs and Symptoms:
- Problems with night vision
- Problems seeing in dim light
- Blind spots in peripheral (side) vision
Later Retinitis Pigmentosa Signs and Symptoms:
- Sensation of twinkling or flashing light
- Tunnel vision (only central vision)
- Sensitivity or discomfort in bright light (photophobia)
- Loss of ability to see color
- Very low vision
What Causes RP?:
Retinitis pigmentosa is caused by changes in certain genes. These genes control the cells that make up your retina.
Tests to Diagnose RP
You may get your eyes examined by an optometrist or an ophthalmologist. Your provider will:
- Ask you to read letters off a chart on the wall
- Ask you to follow objects with your eyes
- Test the pressure in your eyes
- Check your side vision (peripheral vision) with a peripheral field test
- Check how your pupils react to light
- Dilate your pupils with eye drops so they can see inside your eye
- Take images of the retina
Electroretinography (ERG) test
Electroretinography is a test that measures your retina’s response to light.
Optical coherence tomography scan
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a noninvasive test that can measure the thickness of your retina and analyze the retinal integrity.
Fundus autofluorescence test
This type of imaging test is noninvasive and can reveal information about the health of your retinas. It’s used for diagnosis, treatment and monitoring.
Management of RP:
The ways to manage RP include:
- Using low vision aids and assistive devices.
- Using sunglasses and other methods to avoid exposure to too much light. Light may make RP worse.
- Treating associated conditions, such as cystoid macular edema (CME), which may happen with RP.
- Treating cataracts which happens when the lens of your eyes becomes cloudy, with surgery to remove them.
Tips to Prevent vision loss:
- Making and keeping regular appointments with your ophthalmologist.
- Wearing sunglasses and avoiding bright lights.
- Being as healthy as possible by eating right and exercising safely.
- Avoid places with too much light.
- Night vision goggles can help improve night vision by enhancing light levels.
- Low-vision aids such as iris vision come with a dedicated RP Mode designed especially for people with retinitis pigmentosa.
- Some people with retinitis pigmentosa suffer from poor color perception. Color filters may help some individuals distinguish colors better.
- Tinted lenses may help reduce glare and improve contrast sensitivity for some people.
- A healthy diet can reduce your risk of developing retinitis pigmentosa, especially foods that are rich in antioxidants such as vitamin A i.e. dairy products, beef liver and fish oils.
- Avoid eating saturated fatty foods, fried foods and sugary drinks.
- Wear sunglasses with UV protection. Ultraviolet (UV) rays have been linked to increased risk of eye conditions, which can affect people with RP even more than they do in the general population.
- Exercise regularly. Some studies indicate that exercise may play a role in preventing degenerative eye diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa.
- Wear protective eyewear during sports and other activities that could cause injury to your eyes. Even minor eye trauma can lead to further vision loss in people with RP.
Ayurveda Treatment of RP
Treatment principles:
- Treatment is aimed to arrest the progress of the diseases.
- Vata pradana Sannipätika timira chikitsa
- Consider the treatment of Nakulandya.
- Deepana – Pachana oushadhas
- Akshi prasadana oushadhas
- Akshi visesha chikitsa
- Raktaprasadana oushadhas
- Dhatukshayajanya vata roga chikitsa
- Nadi balya oushadhas
- Chakshushya aushadhas
- Psychotherapy
Panchakarma Treatment modalities:
- Snehapana
- Talam
- Nasya (brmhana, prasadana)
- Virechana
- Shiro abyanga
- Shiro lepana
- Shiro dhara
- Shiro vasti
- Anjanam
- Tarpanam
- Putapaka (Snehana)
- Vasti – Chakshushya
Internal medicines:
- Kashaya:
- Amritä shadangam kashaya
- Bala shadangam kashaya
- Jivantyadi gana kashaya
- Mahā manjshthadi kashaya
- Mahatiktakam kashaya
- Pathya shadangam kashaya
- Vidaryadi kashaya
- Arishta / asava:
- Aswagandhärishtam
- Balarishtam
- Drakshärishta
- Vidaryadyāsavam
- Churna:
- Amalaki + yashti churna
- Avipatti cúrna (if virechana is needed)
- Triphala churna
- Swarasa:
- Amalaki swarasa
- Guduchi satwa
- Jivaniya putapaka rasa
- Anjana:
- Churnitanjana
- Kanasaindhavadianjana
- Usiradianjana
- Taila (ext/nasya):
- Bhrigamalakadi taila
- Bhingaraja taila
- Brahmi taila
- Dhanwantaram taila & avartti
- Kayyonnyadi taila
- Kshirabala taila & avartti
- Triphaladi taila
- Ghrita (int/tarpana/nasya):
- Jivaniya gana Ghrita-tarpana & int
- Jivanthyadi Ghrita
- Mahatiktakam Ghrita
- Mahatraiphala Ghrita
- Patoladi Ghrita
- Satahwadi Gritha -tarppana
- Vidaryadi Ghrita
- Lehya:
- Amalaki rasayana
- Aswagandhadi lahya
- Vidäryadi lehyam
- Bhasma:
- Abhraka bhasma
- Kanmada bhasma
- Pravala bhasma
- Rajata bhasma
- Swarna bhasma
- Yashada bhasma
- Rasa/ loha preparations:
- Mahalakshmivilasa rasa
- Saptamrita louha
- Jivaniya putapaka rasa
- Yakrut pippali rasayana
At KPN Ayurveda, we provide the best Retinitis Pigmentosa - Ayurveda Management in Hassan.
